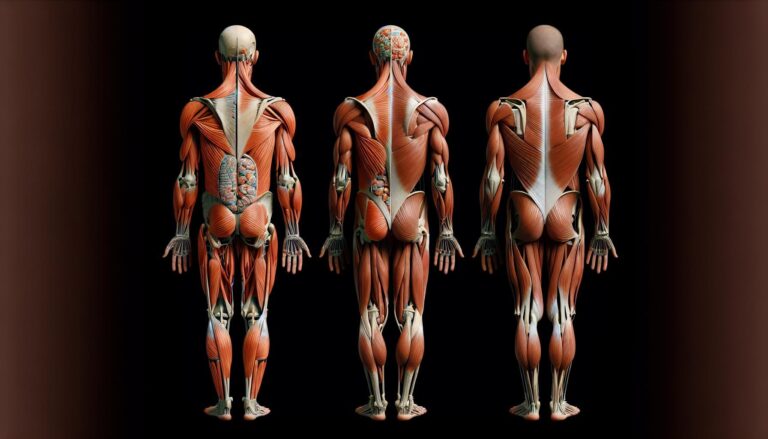
Difference Between Anterior and Posterior refers to two opposing anatomical terms. Anterior denotes the front of the body or an organ, while posterior indicates the back. Understanding this distinction is crucial in fields like anatomy and medicine for accurate communication.
Understanding Anterior and Posterior in Anatomical Terms
In the realm of anatomy, understanding the terms anterior and posterior is crucial for accurately describing the location of various structures in the body. Anterior refers to the front part of the body, while posterior describes the back. This terminology is not merely academic; it plays a vital role in various fields, including medicine, biology, and fitness. For instance, when referring to the position of the heart, we say it is located anterior to the spine, emphasizing its front-facing orientation relative to other structures. This distinction helps clarify spatial relationships in complex anatomical discussions, making it an essential element of human biology.
Additionally, these terms can apply to individual body parts as well as broader anatomical contexts. In practice, many anatomical features have both anterior and posterior aspects. For example, the knee joint can be described in terms of its anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and its posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), which serve distinct functional roles. Recognizing the Difference Between Anterior and Posterior not only aids in comprehending bodily functions but also enhances the ability to communicate effectively about anatomical features among professionals. the distinction plays a significant role in the medical field and in our understanding of human anatomy.
The Role of Anterior and Posterior in Human Anatomy
Understanding the concepts of anterior and posterior is crucial for anyone studying human anatomy, as these terms help define the locations of various structures within the body. Anterior, derived from the Latin word for “before,” refers to the front side of the body. Common examples include the face, chest, and abdomen, all of which are located anteriorly. Conversely, posterior, which means “behind,” refers to the back side of the body. Structures such as the spine, shoulders, and calves are considered posterior. This distinction is essential for clinicians, educators, and students who need to accurately communicate about body parts and their relationships based on position, emphasizing the difference between anterior and posterior in diagnostic and treatment scenarios.
To fully appreciate the difference between anterior and posterior, it’s helpful to visualize their respective locations through examples and anatomical diagrams. For instance, if we compare various body parts, we can see a clear differentiation:
| Body Part | Position |
|---|---|
| Heart | Anterior |
| Spine | Posterior |
| Stomach | Anterior |
| Kidneys | Posterior |
This table serves as a simple reference for key organs, illustrating the distinct locations of anterior and posterior structures. Whether discussing surgical approaches or anatomical relationships, recognizing the difference between anterior and posterior significantly enhances our understanding of the body’s organization and function.
Key Differences in Location and Function
The terms anterior and posterior primarily refer to the location of structures within the body. Anterior, derived from Latin meaning “before,” refers to the front part of the body. Conversely, posterior means “behind,” indicating the back portion. This distinction is particularly crucial in fields like anatomy, where identifying the position of organs or limbs can influence understanding of their function and interactions. For instance, the heart is located anteriorly to the spine, which highlights its positioning that plays a vital role in its function of pumping blood effectively throughout the body.
In terms of function, the difference between anterior and posterior can significantly affect how we approach certain medical conditions or surgical procedures. Anterior structures, such as the chest and abdomen, are often involved in processes that facilitate movement and respiration, while posterior structures like the back and spinal cord are essential for support and protection. Recognizing this difference between anterior and posterior can also aid in effective diagnosis and treatment strategies. Below is a summary of key distinctions:
| Aspect | Anterior | Posterior |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Front of the body | Back of the body |
| Function | Involved in respiration and movement | Provides structural support and protection |
| Examples | Heart, chest | Spine, muscles of the back |
Understanding the difference between anterior and posterior not only serves anatomical education but also reinforces its importance in clinical practices. By correctly identifying these positions, healthcare professionals can better communicate about anatomy, describe symptoms, and ensure comprehensive patient care. Thus, acknowledging the distinct roles that anterior and posterior areas play can enhance our overall comprehension of bodily function and improve health outcomes.
Exploring Anterior and Posterior Positions in Daily Activities
Understanding the difference between anterior and posterior positions can greatly enhance our awareness of body mechanics in everyday activities. For instance, when you are sitting at a desk, your knees are in an anterior position relative to your hips, while your back rests in a posterior position. This spatial awareness can help inform adjustments to your posture, leading to improved comfort and reduced strain. Engaging in activities like cycling or running further exemplifies these concepts. As you pedal or stride, your feet move in an anterior direction while your glutes work from a more posterior stance, illustrating the dynamic interplay between these two positions.
Moreover, the difference between anterior and posterior can be observed in simple yet vital tasks such as lifting objects. When squatting to pick something up, ensuring your chest remains anterior to your knees helps maintain a straight back and promotes safety. On the other hand, when leaning over to retrieve an item, your torso shifts into a more posterior position. By being conscious of these positions, we can apply this knowledge to enhance physical activities and minimize the risk of injury, ultimately transforming our daily routines into opportunities for better health and well-being.
Clinical Implications of Anterior and Posterior Definitions
The distinction between anterior and posterior definitions is crucial in various clinical settings, as it directly impacts diagnostic approaches, treatment strategies, and surgical outcomes. In the context of anatomy, anterior refers to the front or forward-facing aspect, while posterior refers to the back or rear aspect. Understanding these terms is particularly vital for health professionals when analyzing imaging results, conducting physical examinations, or performing surgical procedures. Misinterpretation of these terms can lead to incorrect diagnoses or inappropriate treatment plans, emphasizing the importance of clarity in communication among healthcare providers and between providers and patients.
To highlight the clinical implications of the Difference Between Anterior and Posterior, consider the following points:
- Diagnostic Imaging: Accurate identification of structures is necessary for effective interpretation of X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
- Surgical Approaches: Knowledge of anterior versus posterior anatomy can dictate the surgical route taken to minimize complications.
- Rehabilitation Protocols: Tailored rehabilitation strategies are often influenced by whether an injury is located in an anterior or posterior position.
Moreover, the table below illustrates various clinical applications pertaining to the Difference Between Anterior and Posterior definitions:
| Clinical Aspect | Anterior | Posterior |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Assessment of lung sounds | Evaluation of spine alignment |
| Surgical Intervention | Hip surgery (anterior approach) | Knee arthroscopy (posterior approach) |
| Treatment Focus | Shoulder stability | Back pain management |
Ultimately, a firm grasp of the Difference Between Anterior and Posterior concepts enhances the precision of clinician assessments and fosters superior patient care outcomes.
Anterior vs. Posterior: A Look at Movement Mechanics
Understanding the difference between anterior and posterior movement mechanics is essential in various fields, including anatomy, physical therapy, and sports science. Anterior refers to the front side of the body, while posterior denotes the back. This distinction plays a critical role in how different muscle groups engage during activities. For instance, movements like squats primarily target the posterior chain, which includes the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back. Conversely, exercises that emphasize the anterior, such as push-ups and bench presses, primarily engage the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
In the realm of biomechanics, the difference between anterior and posterior is often quantified in terms of force production and range of motion. The anterior muscles are generally associated with flexion and lifting actions, whereas the posterior muscles facilitate extension and stabilization. Understanding this dynamic can help optimize training programs and injury prevention strategies. Here’s a simple comparison table to illustrate key points:
| Aspect | Anterior | Posterior |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Flexion and lifting | Extension and stabilization |
| Examples of Exercises | Push-ups, Bench Press | Squats, Deadlifts |
| Common Injuries | Shoulder injuries | Lower back pain |
Recognizing the difference between anterior and posterior mechanics not only impacts performance but also plays a crucial role in rehabilitation settings. Therapists often design programs that target specific movements based on whether they require anterior or posterior focus. A balanced approach addressing both areas can lead to improved strength and coordination, ultimately enhancing overall physical health. Incorporating awareness of these mechanics into daily activities can also aid in injury prevention, ensuring that individuals maintain their physical well-being.
Understanding Anterior and Posterior in Different Disciplines
In biology and anatomy, the terms anterior and posterior are essential for describing the relative positions of structures in a body. Anterior refers to the front side, while posterior denotes the back. This distinction helps in various fields, such as medicine and zoology, where understanding the orientation of body parts is crucial. For instance, in human anatomy, the nose is anterior to the ears, emphasizing the clear spatial relationship necessary for effective communication in healthcare settings. Similarly, in veterinary medicine, recognizing the difference between anterior and posterior in animals aids in surgeries and veterinary diagnostics.
Transitioning to disciplines like art and architecture, the concepts of anterior and posterior can apply metaphorically to the arrangement of elements within a composition. The anterior elements often draw the viewer’s attention first, acting as the focal point, whereas the posterior elements serve as a backdrop that supports the primary subject. This strategic placement creates depth and dimension in a piece. Analyzing how these terms are utilized in different contexts illustrates the broad applicability of the difference between anterior and posterior, showcasing how they serve not only as anatomical references but also as tools for creative expression across various fields.
Common Misconceptions: Clarifying Anterior and Posterior
Understanding the terms anterior and posterior can sometimes lead to confusion, particularly in medical and anatomical contexts. One common misconception is that these terms refer exclusively to the front and back of the body, respectively. While it is true that anterior means situated in the front and posterior denotes the back, the application of these terms can vary based on the specific context. For instance, in animals, what is considered anterior or posterior can differ depending on their orientation. Thus, grasping the difference between anterior and posterior is vital for accurate communication, especially in scientific discussions.
Another misunderstanding arises when people assume that anterior and posterior apply uniformly to all body parts. In truth, these terms can take on different meanings depending on the region of the body being discussed. For example, in humans, the anterior aspect of the body includes features like the face and chest, while the posterior encompasses the back and glutes. Moreover, the difference between anterior and posterior is not limited to humans; it also extends to how quadrupeds refer to their limbs and organs. Here’s a quick reference table to illustrate the distinctions clearly:
| Feature | Anterior | Posterior |
|---|---|---|
| Human Body | Face, Chest | Back, Glutes |
| Quadrupeds | Head, Front Legs | Tail, Hind Legs |
By clarifying these common misconceptions around the difference between anterior and posterior, one can communicate more effectively in fields such as biology, medicine, and fitness. Misinterpretations can lead to confusion during diagnoses or anatomical discussions, emphasizing the importance of clear distinctions in terminology.
Recommendations for Proper Posture and Movement
Maintaining proper posture and movement is essential for overall physical well-being and can significantly impact your understanding of the Difference Between Anterior and Posterior. Start by ensuring that your spine is aligned when sitting or standing. Imagine a straight line running from the top of your head, through your shoulders, down to your hips, providing a stable base to promote healthy bodily mechanics. Here are some tips to encourage good posture:
- Engage your core: This stabilizes your trunk and supports your spine.
- Keep your shoulders back: Avoid slouching by gently rolling your shoulders into a comfortable position.
- Align your head: Keep your ears over your shoulders to prevent forward head posture.
Movement patterns also play a critical role in differentiating between anterior and posterior body mechanics. When engaging in physical activity, focus on using your entire body rather than relying too heavily on specific muscle groups. This balanced approach not only aids in movement efficiency but also reinforces your understanding of the Difference Between Anterior and Posterior in relation to muscle engagement. Consider these movement strategies:
- Maintain a neutral spine: This prevents excessive strain on your back.
- Incorporate leg and hip movement: This assists in lifting and bending.
- Practice dynamic stretching: This promotes flexibility and prepares muscles for activity.
| Posture Tips | Movement Strategies |
|---|---|
| Align your spine | Use full-body movements |
| Engage your core | Maintain a neutral spine |
| Keep shoulders back | Incorporate hip movement |
The Significance of Anterior and Posterior in Physical Therapy
Understanding the difference between anterior and posterior is crucial for both patients and practitioners in the field of physical therapy. The terms dictate the positioning and approach of various therapeutic interventions. For instance, injuries or conditions involving the anterior compartment of the body—like the front of the knees or shoulders—often require specific stretching and strengthening exercises to improve functionality. Conversely, assessments focusing on the posterior aspect—such as the back or hamstrings—demand unique treatment modalities. Recognizing these distinctions helps therapists develop comprehensive treatment plans tailored to a patient’s specific needs.
In practice, the distinction impacts assessment techniques, exercise selection, and therapeutic outcomes. Practitioners often utilize various tools and techniques to address the issues related to each area effectively. Below are some considerations made based on the Difference Between Anterior and Posterior:
- Anterior Focus: Emphasis on quadriceps and hip flexors.
- Posterior Focus: Attention to hamstrings and spinal alignment.
- Rehabilitation Strategies: Tailored exercise programs for anterior or posterior injuries.
- Assessment Techniques: Tests that isolate movements in the anterior or posterior positions.
| Body Region | Common Issues | Therapeutic Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Anterior | Knee Pain, Shoulder Strain | Strengthening, Flexibility Exercises |
| Posterior | Back Pain, Hamstring Strain | Stability, Posture Correction |
By appreciating the difference between anterior and posterior, therapists can foster improved recovery pathways and enhance overall patient care. The clarity of these terms and their associated practices not only aids in diagnosis but also enriches the therapeutic alliance between the patient and their caregiver. Ultimately, this deeper understanding of the Difference Between Anterior and Posterior empowers effective, targeted rehabilitation strategies tailored to each individual’s circumstances.
Visual Aids: Enhancing Understanding of Anterior and Posterior
Visual aids can transform the way we grasp the difference between anterior and posterior. By employing diagrams, infographics, and 3D models, learners can gain a comprehensive understanding of these anatomical terms, which describe locations in the body. For instance, a simple diagram highlighting the face of a cat, showcasing the anterior position as the front (where the eyes and mouth are), and the posterior position as the back (highlighting the tail), offers clear visual discrimination. This form of learning lays the groundwork on which students can build upon, facilitating better retention and application.
Moreover, tables and charts effectively summarize the difference between anterior and posterior in various contexts. Consider the following table that succinctly outlines some anatomical examples and their respective positions:
| Anatomical Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Anterior | Refers to the front of the body or structure. |
| Posterior | Refers to the back or rear of the body or structure. |
| Example | The nose is anterior to the ears. |
Using these visual elements as teaching tools will not only enhance comprehension but also provide clarity when exploring the difference between anterior and posterior in various biological and medical contexts. As learners engage with these visuals, they can better visualize spatial relationships within the human body and appreciate the importance of precise terminology in fields such as anatomy and medicine.
Real-Life Examples: Applications of Anterior and Posterior Concepts
Understanding the distinction between anterior and posterior is essential in various fields, such as medicine, biology, and even in everyday scenarios. For instance, in anatomical studies, the anterior refers to structures located at the front of the body, such as the face or chest, while the posterior indicates areas toward the back, such as the spine or glutes. This differentiation plays a critical role not only in anatomical vocabulary but also in the diagnosis and treatment of injuries. If a patient presents with pain in the posterior region, it can signify issues related to the spine or lower back, impacting treatment plans. Such applications underscore the practical implications of the difference between anterior and posterior in clinical assessments.
In the realm of technology, especially in robotics and animation, the concepts of anterior and posterior find application in the movement and positioning of robots or animated characters. When programming a robot, the anterior might be designated as the front-facing part where sensors are located, while the posterior might be where power sources are situated. This spatial awareness enhances functionality in navigation and task execution. In animation, understanding these terms allows animators to create more lifelike movements by ensuring characters have coherent anatomical gestures that mirror the natural difference between anterior and posterior. The integration of these concepts across different domains is a testament to their fundamental importance in enhancing clarity and effectiveness in communication and application.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What do the terms ”anterior” and “posterior” refer to in anatomical terminology?
A: In anatomical terminology, “anterior” refers to the front part of the body, while “posterior” refers to the back part. These terms help clearly define the position of structures in relation to each other.
Q: Why are these terms important in anatomy?
A: Anterior and posterior provide a universal language for medical professionals, enabling clear communication about the location of organs, muscles, and other structures. This precision is crucial in fields such as medicine, biology, and even physical therapy.
Q: Can you give an example of an anterior structure?
A: Certainly! The chest is considered anterior because it lies at the front of the torso. Another example would be the nose, which is positioned at the front of the face.
Q: What about a posterior example?
A: The back is categorized as posterior; for instance, the spine is positioned at the posterior aspect of the torso. Additionally, the heel of the foot is located posteriorly compared to the toes.
Q: How do these terms work in everyday language outside of anatomy?
A: Outside of anatomical contexts, “anterior” and ”posterior” can also be applied metaphorically. For instance, we might refer to the “anterior” part of a project as the front-facing aspects, like presentations and promotions, while the “posterior” could refer to the behind-the-scenes work, such as planning and execution.
Q: Are anterior and posterior synonymous with other directional terms?
A: Not quite; while they both provide insight into position, they are specific to front and back. Other directional terms include “medial” (toward the midline) and “lateral” (away from the midline), which help further specify locations in relation to the body’s center.
Q: How do anterior and posterior relate to other disciplines like ecology or engineering?
A: In ecology, these terms may be used to describe the positions of organisms or structures in a spatial context. In engineering, particularly in robotics, “anterior” and “posterior” can describe the orientation of parts or components based on their placement in relation to the rest of the machine or design.
Q: Is it important to always remember the difference between these two terms?
A: Yes, maintaining an understanding of anterior and posterior is crucial, especially in fields that require precise descriptions of bodily structures or where spatial awareness is key, such as surgery or anatomy studies. This knowledge enhances clarity and effectiveness in communication.
Q: How can one master the use of these terms?
A: Through consistent practice and application! Engaging with anatomical texts, diagrams, or even patients in a clinical setting can reinforce your understanding. Visual aids can help solidify the concept, making it easier to recall the definitions in relevant contexts.
In Summary
understanding the difference between anterior and posterior is essential for clear communication in anatomy and related fields. By distinguishing between these two terms, you can enhance your comprehension of spatial relationships in the body. Remember, mastering the difference between anterior and posterior contributes significantly to your overall knowledge.